
8 In this article, I have attempted to use the less-emotive term “d-block element”. However, these terms are, at least in English, neologisms dating to the second decade of the last century.
DIFFERENT BLOCKS IN PERIODIC TABLE SERIES
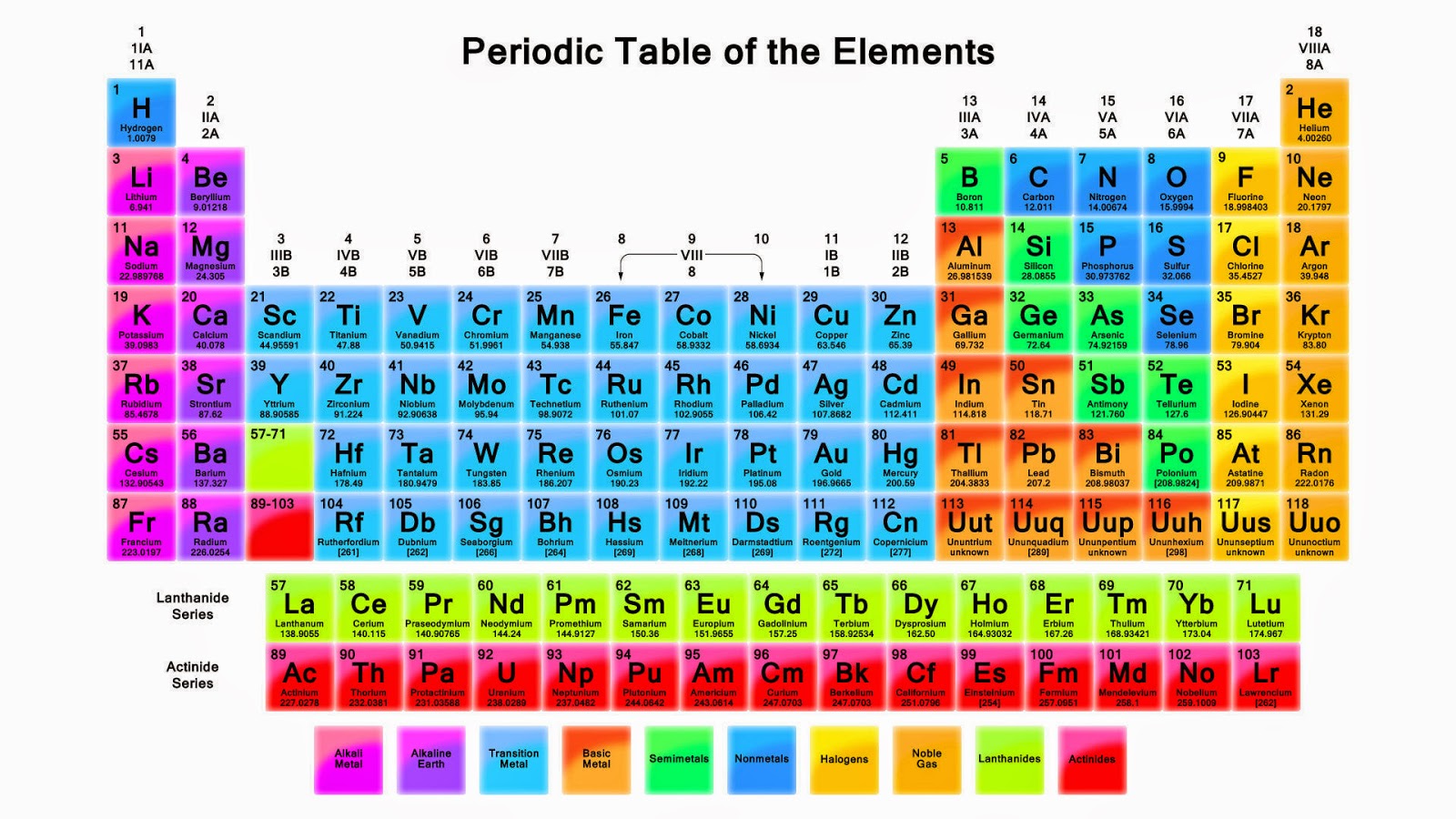
Today we use the terms transition metal, transition series and transition element interchangeably and with an implicit understanding of which elements they refer to. This article provides an overview of how the elements in groups 3–12 influenced the development and refinement of our modern periodic table. However, many of these elements are scientific newcomers and their history is, in a way, also the history of the development of the periodic table. They continue to lie at the forefront of research in areas as diverse as materials science, catalysis, bioinorganic chemistry, materials science and photonic materials. These elements have played a critical rôle in our understanding of modern chemistry and have proved to be the touchstones for many theories of valence and bonding. In the commonly encountered medium or long forms of the periodic table, the central portion is occupied by the d-block elements, commonly known as the transition elements or transition metals.

1 The modern medium length form of the periodic table (). The arrangement of objects and concepts in rows and columns appeals to mankind's search for order in his world, and periodic tables concerning objects as diverse as fruit, vegetables, beer, cartoon characters, and superheroes abound in our connected world. 6 It is only necessary to sketch the block structure of the periodic table for an audience to exhibit enlightenment and recognition. 5 However, the periodic table has achieved a cultural identity that far transcends its scientific relevance and has become one of the iconic scientific symbols recognized worldwide in all levels of society. 4 The naming of elements after prominent scientists also generated debate with the proposal to name element 106 Seaborgium, after Glenn Seaborg, which transgressed a previously unwritten (and unobserved in the case of einsteinium) rule that elements were not to be named after living researchers. 3 The latter task acquired a decidedly political aspect as the search for new elements became linked with cutting edge physics in the race for dominance in nuclear technologies. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is trusted with the custodianship of the periodic table and acts as the arbiter for the validation and nomenclature of new elements as well as providing the definitive list of the atomic weight of all elements. 2 A chemist can look at the periodic table and gain a deep understanding of the chemical relationships between elements and make reasoned predictions of chemical behaviour on the basis of the position within the table and the implied arrangement of valence shell electrons. 1 The periodic table lies at the core of our understanding of the properties of, and the relationships between, the 118 elements currently known ( Fig. Introduction In the year 2019 we celebrate the sesquicentennial of the publication of the first modern form of the periodic table by Mendeleev (alternatively transliterated as Mendelejew, Mendelejeff, Mendeléeff, and Mendeléyev from the Cyrillic ). On the occasion of the sesquicentenniel of the discovery of the periodic table by Mendeleev, it is appropriate to look at how these metals have influenced our understanding of periodicity and the relationships between elements. The d-block elements have played an essential role in the development of our present understanding of chemistry and in the evolution of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
